- InstaByte
- Posts
- Elon killed GPT. But Gemini won.
Elon killed GPT. But Gemini won.
ALSO: Database Sharding Strategies

Welcome back!
This week's problem will twist your brain in knots. But once you understand it, the solution is surprisingly simple. All the best!
Today we will cover:
Copy List with Random Pointer
Database Sharding Strategies
Read time: under 4 minutes
CODING CHALLENGE
Copy List with Random Pointer
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representing Node.val
random_index: the index of the node (range from 0 to n-1) that the random pointer points to, or null if it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:
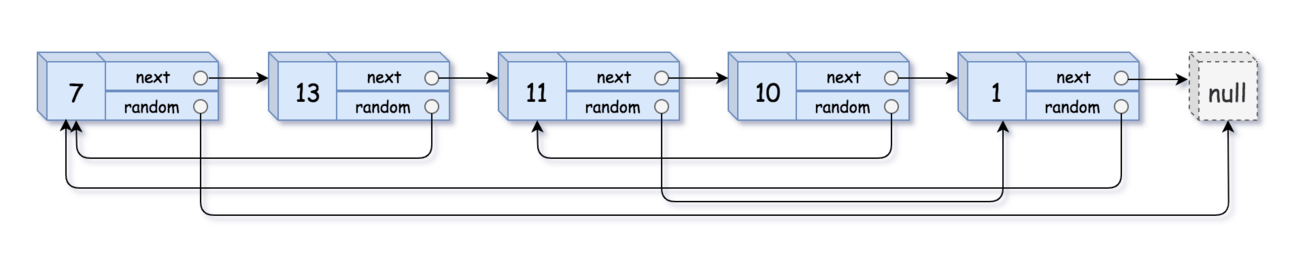
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]Example 2:
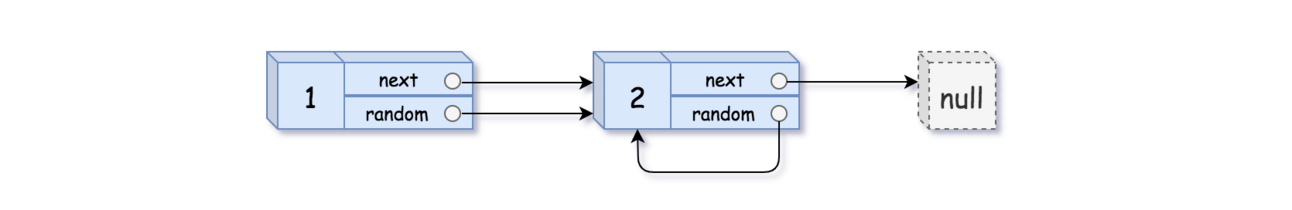
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]Solve the problem here before reading the solution.
PRESENTED BY MINDSTREAM
Choose the Right AI Tools
With thousands of AI tools available, how do you know which ones are worth your money? Subscribe to Mindstream and get our expert guide comparing 40+ popular AI tools. Discover which free options rival paid versions and when upgrading is essential. Stop overspending on tools you don't need and find the perfect AI stack for your workflow.
SOLUTION
To solve this problem, we'll use a hash map to create a deep copy of the linked list while maintaining the original list's structure. The hash map will help us map original nodes to their corresponding new nodes.
We'll do this in two passes:
First, create new nodes and map original nodes to their copies.
Then, set the next and random pointers for the new nodes.
This approach ensures that we create a completely independent copy of the original linked list, with new nodes that have the same values and pointer relationships.
The time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. We make two passes through the list.
The space complexity is also O(n) due to the hash map storing node mappings.

WANT PRIVATE EMAIL?
Free, private email that puts your privacy first
Proton Mail’s free plan keeps your inbox private and secure—no ads, no data mining. Built by privacy experts, it gives you real protection with no strings attached.
SYSTEM DESIGN
Database Sharding Strategies
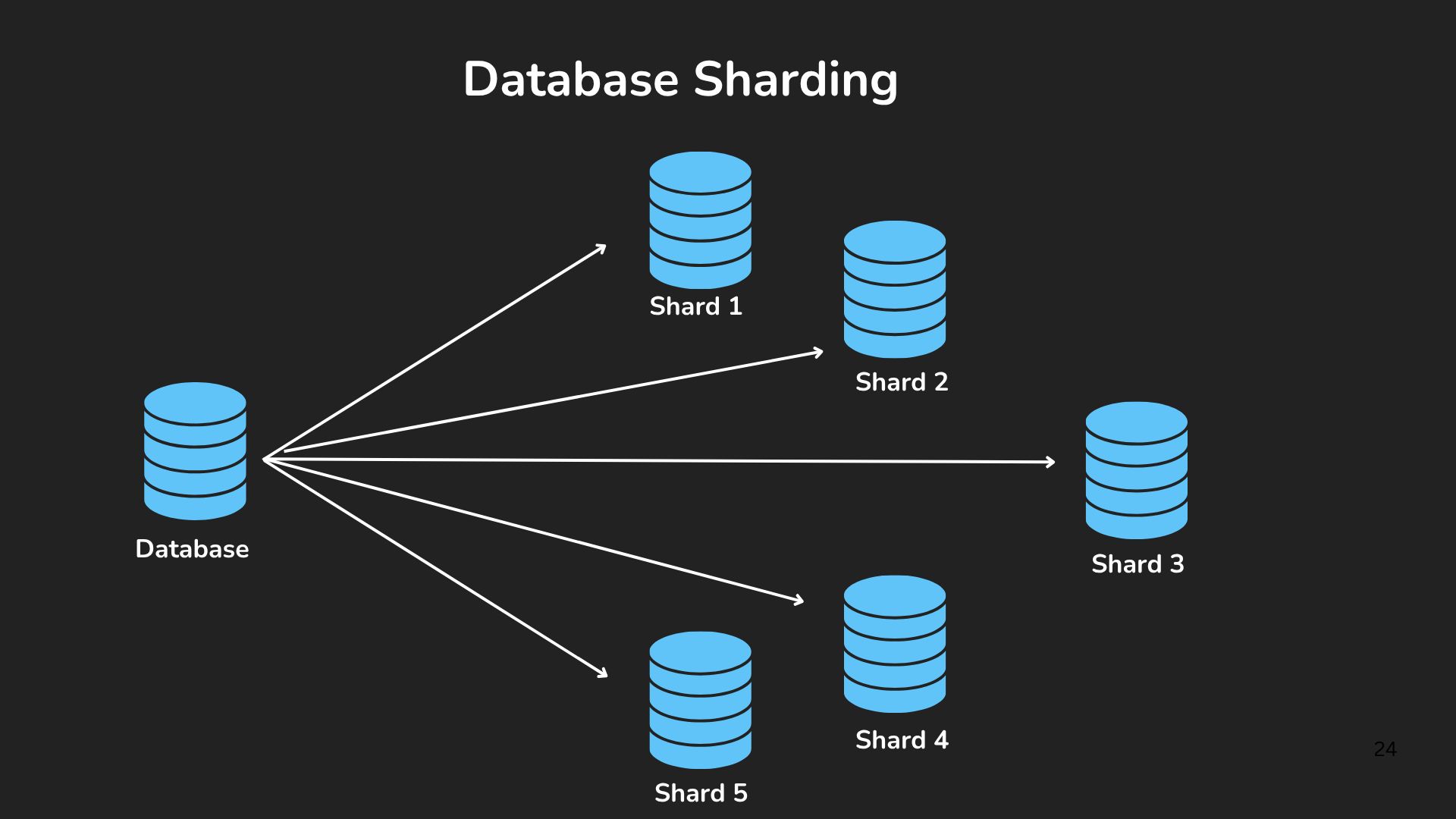
As your application grows, a single database server might struggle to handle all the data and user requests. Database sharding solves this by splitting your data across multiple servers, but choosing the right sharding strategy is crucial for performance.
Range-based Sharding divides data based on ranges of a specific field. For example, if you're storing user data, you might put users with IDs 1-1000000 on one server, 1000001-2000000 on another, and so on. This strategy works well when you need to retrieve data within specific ranges, like finding all orders from the last month. However, if the chosen ranges aren't balanced, some servers might end up with more traffic than others.
Hash-based Sharding uses a hash function to determine which server stores each piece of data. When storing user data, you might hash the user ID and use the result to pick a server. Hash-based sharding typically distributes data more evenly than range-based sharding, but it makes range queries harder since related data might be spread across different servers.
Geographic Sharding stores data on servers physically closest to where it's most frequently accessed. For a social media platform, European users' data might be stored on servers in Europe, while Asian users' data stays on Asian servers. This reduces latency but can complicate data access when users interact across regions.
Here's a comparison of these strategies:
Strategy | Data Distribution | Range Queries | Geographic Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
Range-based | Can be uneven | Efficient | Not optimized |
Hash-based | Even | Inefficient | Not optimized |
Geographic | Based on location | Moderate | Highly efficient |
The choice of sharding strategy depends on your specific needs. Range-based sharding works well for time-series data, hash-based sharding is great for evenly distributed workloads, and geographic sharding shines in global applications where latency matters.
FEATURED COURSES
5 Courses of the Week
✅ 100 Days of Code - The Complete Python Pro Bootcamp: Comprehensive 60+ hour Python course building 100 projects including games, web apps, automation tools, and data science projects, covering everything from basics to professional development with Flask, APIs, databases, and deployment.
✅ React - The Complete Guide: Comprehensive 40+ hour React course covering fundamentals through advanced concepts including hooks, routing, Redux, Next.js, TypeScript, authentication, and testing, with hands-on projects and updated for React 19 features.
✅ Java Masterclass: Beginner-friendly Java course taught by Oracle-certified experts, covering fundamentals through advanced topics with hands-on coding notebooks and practical examples to prepare students for Java programming jobs and freelance opportunities.
✅ Python Programming for AI: Build Python fundamentals for AI using NumPy, pandas, and Matplotlib, then progress to machine learning models, PyTorch neural networks, deep learning frameworks, and generative AI with Transformers for natural language processing applications.
✅ Reinforcement Learning Course: Learn AI foundations behind ChatGPT and GPT-4, covering multi-armed bandits, Markov Decision Processes, Q-Learning, and approximation methods with hands-on implementation from scratch including a stock trading bot project.
NEWS
This Week in the Tech World

Gemini 3 Released: Google has released Gemini 3, its most powerful AI model yet. The update brings advanced reasoning, autonomous coding tools, and interactive search.
xAI Launches Grok 4.1: xAI released Grok 4.1 with improved reasoning and reduced hallucinations. The update adds an Agent Tools API for building autonomous agents.
OpenAI Releases GPT-5.1: OpenAI has launched GPT-5.1, giving users more control over ChatGPT's tone and style. The update aims to refine the AI's personality and responses.
Google Debuts Antigravity: Google unveiled Antigravity, a new agentic development platform. The tool focuses on coding productivity over hype, offering robust autonomous help.
Chrome Zero-Day Found: Google warns users to update Chrome immediately to fix a severe zero-day flaw. Attackers are actively exploiting the vulnerability in the wild.
LeCun Leaves Meta AI: Meta confirmed AI Chief Yann LeCun is leaving to found a startup. The move marks a significant shift for Meta's AI leadership and future strategy.
BONUS
Just for laughs 😏
HELP US
👋 Hi there! We are on a mission to provide as much value as possible for free. If you want this newsletter to remain free, please help us grow by referring your friends:
📌 Share your referral link on LinkedIn or directly with your friends.
📌 Check your referrals status here.
YOUR FEEDBACK
What did you think of this week's email?Your feedback helps us create better emails for you! |
Until next time, take care! 🚀
Cheers,


