- InstaByte
- Posts
- OpenAI shocks everyone, again!
OpenAI shocks everyone, again!
ALSO: Authentication Methodologies

Welcome back!
Everyone knows how to reverse a LinkedList. But this week's challenge adds a twist that changes everything.
Today we will cover:
Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Authentication Methodologies
Read time: under 4 minutes
CODING CHALLENGE
Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Given the head of a linked list, reverse the nodes of the list k at a time, and return the modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:

Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output: [2,1,4,3,5]Example 2:
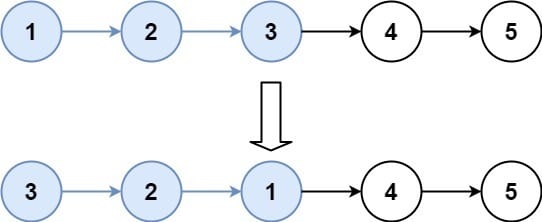
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
Output: [3,2,1,4,5]Solve the problem here before reading the solution.
PRESENTED BY THE CODE
Find out why 100K+ engineers read The Code twice a week
Staying behind on tech trends can be a career killer.
But let’s face it, no one has hours to spare every week trying to stay updated.
That’s why over 100,000 engineers at companies like Google, Meta, and Apple read The Code twice a week.
Here’s why it works:
No fluff, just signal – Learn the most important tech news delivered in just two short emails.
Supercharge your skills – Get access to top research papers and resources that give you an edge in the industry.
See the future first – Discover what’s next before it hits the mainstream, so you can lead, not follow.
SOLUTION
To solve this problem, we'll use an iterative approach that reverses groups of k nodes while maintaining the overall structure of the list.
We'll use a helper function to reverse a portion of the linked list and keep track of the groups of k nodes. If the remaining nodes are less than k, we'll leave them as they are.
Here is how the solution works:
We use a dummy node to handle changes in the list's head
We check if we have
knodes to reverseWe use a separate helper function
reverseto reverse a portion of the listWe keep track of the previous group, current group, and next group
After reversing, we reconnect the groups
If there are fewer than
knodes remaining, we leave them as they are
The time complexity of this solution is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.

HEARD OF THE DEEP VIEW?
Stop Drowning In AI Information Overload
Your inbox is flooded with newsletters. Your feed is chaos. Somewhere in that noise are the insights that could transform your work—but who has time to find them?
The Deep View solves this. We read everything, analyze what matters, and deliver only the intelligence you need. No duplicate stories, no filler content, no wasted time. Just the essential AI developments that impact your industry, explained clearly and concisely.
Replace hours of scattered reading with five focused minutes. While others scramble to keep up, you'll stay ahead of developments that matter. 600,000+ professionals at top companies have already made this switch.
SYSTEM DESIGN
Authentication Methodologies

Building secure applications requires robust user authentication. Let's look at different ways to authenticate users and understand when to use each method.
Password-based authentication is the most common method. Users provide a username and password which is checked against stored credentials. While simple to implement, this method has limitations. Users often choose weak passwords or reuse them across sites. To make password authentication more secure, you can add requirements for password complexity and implement rate limiting to prevent brute force attacks.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security. After entering their password, users must provide a second form of verification. This could be a code sent via SMS or generated by an authenticator app. 2FA significantly improves security because even if attackers steal a password, they can't access the account without the second factor.
Token-based authentication uses temporary access tokens instead of sending credentials with every request. When users log in, they receive a token (usually a JWT) that they include in subsequent requests. Tokens can contain user information and permissions, and they automatically expire after a set time. This makes token-based auth ideal for modern web applications and APIs.
OAuth is used for authorizing applications to access user data on other platforms. For example, when you "Login with Google," you're using OAuth. The application gets a token to access your Google data without ever seeing your Google password. OAuth is perfect when you want to integrate with other services or provide "Sign in with X" functionality.
FEATURED COURSES
5 Courses of the Week
✅ Stanford’s Algorithms Specialization: Master fundamental algorithms through programming assignments and conceptual learning. This specialization prepares you to excel in technical interviews and communicate fluently about algorithms without focusing on low-level implementation details.
✅ Grokking the Modern System Design Interview: Get hands-on practice with over 100 data structures and algorithm exercises and guidance from a dedicated mentor to help prepare you for interviews and on-the-job scenarios.
✅ DeepLearning.AI Data Engineering Certificate: Build data pipelines on AWS, design data architectures, and learn batch/streaming processing. Hands-on labs with real-world tools.
✅ IBM’s Intro to Containers w/ Docker, Kubernetes & OpenShift: Learn to build and run applications using containers with Docker, and manage them at scale with Kubernetes and OpenShift. Get hands-on experience through browser-based labs.
✅ Firebase in a Weekend (Android): This course will teach you when and why to choose Firebase as a backend for your Android application.
NEWS
This Week in the Tech World

OpenAI Sora 2 Released: OpenAI launched Sora 2, the next generation of its text-to-video AI model with improved video generation capabilities. The model allows users to create realistic videos from text prompts with better quality and control than its predecessor.
Claude Sonnet 4.5 Debuts: Anthropic released Claude Sonnet 4.5, claiming it's the best coding model available. The model can work autonomously for 30+ hours, scoring 77.2% on SWE-bench software engineering tests and outperforming GPT-5.
DeepSeek Releases V3.2-Exp: Chinese AI company DeepSeek unveiled V3.2-Exp, an experimental model with improved efficiency and 50% lower API costs. The release follows DeepSeek's Nature paper revealing R1 training cost just $294,000, challenging assumptions about expensive AI development.
npm Worm Compromises 500+ Packages: Self-replicating malware dubbed "Shai-Hulud" infected 500+ npm packages including @ctrl/tinycolor and CrowdStrike libraries. The worm steals credentials and automatically spreads to other packages. GitHub responded by blocking uploads and removing compromised packages.
PostgreSQL 18 Ships: PostgreSQL 18 was released, featuring a new asynchronous I/O subsystem delivering up to 3x performance improvements. The release includes better indexing, faster major-version upgrades, virtual generated columns, and OAuth 2.0 authentication support for easier SSO integration.
DoorDash unveils delivery robot Dot: Food delivery giant launches autonomous robot reaching 20 mph carrying 30 pounds for Phoenix merchants. Bot uses eight cameras and lidar sensors while SmartScale feature cuts missing item complaints by 30%.
Microsoft touts "vibe working" for Office: Company adds AI agent mode to Excel and Word letting users describe desired outputs iteratively. Copilot manages 57% accuracy versus human's 71% on spreadsheets, requiring careful auditing.
BONUS
Just for laughs 😏

HELP US
👋 Hi there! We are on a mission to provide as much value as possible for free. If you want this newsletter to remain free, please help us grow by referring your friends:
📌 Share your referral link on LinkedIn or directly with your friends.
📌 Check your referrals status here.
YOUR FEEDBACK
What did you think of this week's email?Your feedback helps us create better emails for you! |
Until next time, take care! 🚀
Cheers,


